Are you ready to introduce yourself?
Show the world what you're made of 💪
Effortlessly showcase your accomplishments because being awesome 😎 deserves a spotlight.
Create
Effortlessly build an online portfolio to showcase your accomplishments.
Share
Share your online portfolio and broadcast your successes to the world.
Connect
Expand your professional circle and forge meaningful relationships.
Building Your Career, One CV at a Time
Create Your Professional CV
Say goodbye to the hassle of manual formatting and updates, and start elevating your professional journey with Briefcase's automatic CV generator.
Seamlessly convert your achievements, skills, and experiences into a polished document suitable for job applications, interviews, and networking.

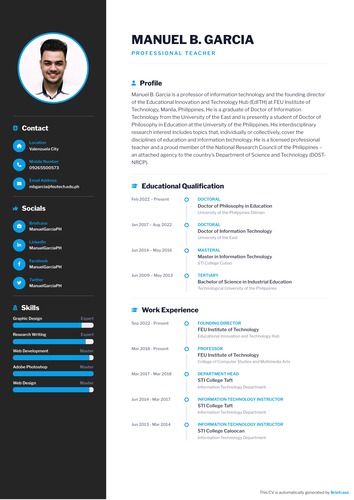
Streamlined Process
Save time and effort by automatically converting your online portfolio content into a well-structured CV.
Professional Formatting
Your CV will maintain a professional look and feel, ensuring you make a strong impression on potential employers.
Versatile Usage
Use your CV for job applications, networking, or any situation where you need to showcase your qualifications.
Always Up-to-Date
Your CV stays current with your latest achievements as you update your portfolio, eliminating the need for manual updates.
Spotlight on Briefcase Users
Here are a few of the incredible tamaraws who have embraced our platform to showcase their skills and accomplishments.
Jace Jacob G. Pasia
BSITCST student at FEU Institute of Technology
Tristan Kenneth S. Marcellana
BSCE student at FEU Alabang
Katherine B. Sazon
BSITSMBA- FEU Institute of Technology
Jehiel T. Fernandez
BSME student at FEU Alabang
Maria Katherine D. Sibayan
William V. Yao
BSITWMA student at FEU Institute of Technology
Ma. Ruth S. Que
Academic Director for Humanities, Social Sciences and Communication Department (HSC)
John Clarenze Lumogdang
BSCPE student at FEU Institute of Technology
Frequently Asked Questions
Ready to show the world?
Join the movement of tamaraws who showcase their accomplishments and show the world what they're made of.
Get started — it’s freeJoin 15663 tamaraws today and start showcasing.

